
All too often, production halts due to tooling incidents. Operators can’t find the required tools during changeovers, tools are broken or missing, and so on. However, most of these problems are avoidable with an effective tool management system.
Tool management, also called “tooling management,” plays a critical role in a manufacturing facility. Ensuring that the right tools are available, in the right condition, and at the right time for each production process.
Let’s take a closer look at the ins and outs of modern tool management, best practices for organizing and tracking tools, and digital tool management solutions.
What is tool management?
Manufacturing tool management is the systematic process of organizing, tracking, and maintaining the tools and equipment used to produce distinct items or assemblies. This can encompass various tasks and processes, including the selection, procurement, storage, allocation, maintenance, and disposal of tools.
The purpose of tool management is to make sure the right tools are available at the right time and in the right condition, especially when you have hundreds or even thousands of tools. A successful digital tool management system minimizes downtime, optimizes tool utilization, and reduces costs associated with tooling processes.
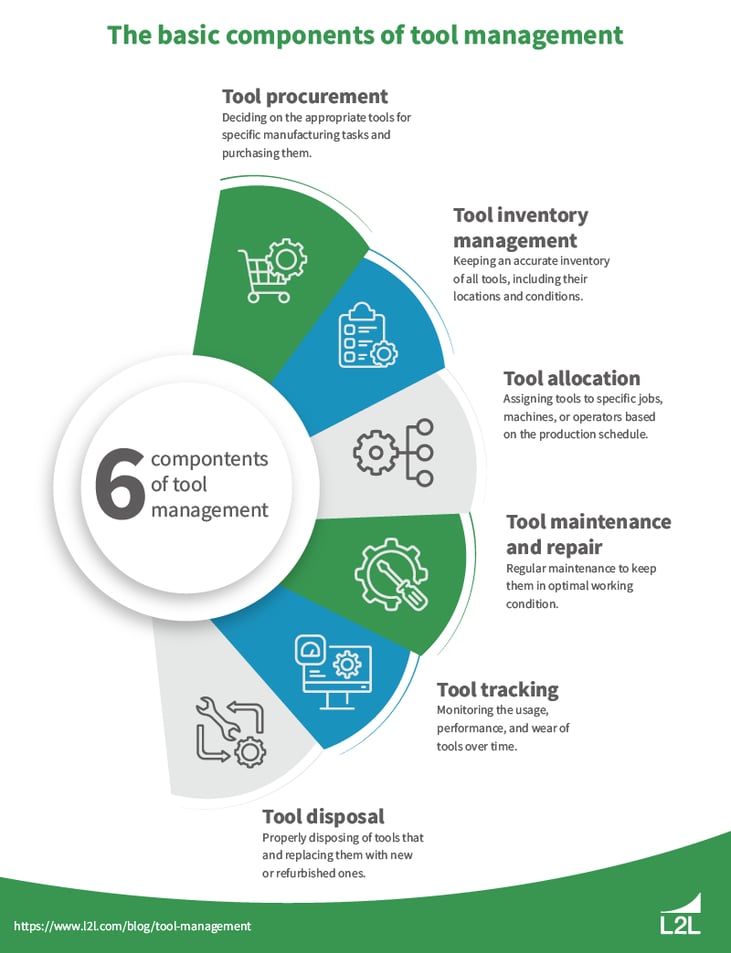
The basic aspects of tooling management include:
-
Tool selection and procurement: Deciding on the appropriate tools for specific manufacturing tasks and purchasing them. This involves considering factors such as tool quality, compatibility with existing machinery, performance specifications, and cost.
-
Inventory management: Keeping an accurate inventory of all tools, including their locations and conditions. This helps prevent tool shortages, overstock situations, and misplacement, ensuring tools are readily available when needed.
-
Tool allocation and scheduling: Assigning tools to specific jobs, machines, or operators based on the production schedule. Efficient tool allocation helps in optimizing workflow and reducing idle time.
-
Maintenance and repairs: Regular maintenance and prompt repairs of tools to keep them in optimal working condition. This includes tasks such as cleaning, sharpening, calibration, and replacing worn or damaged parts, which helps in extending tool life and ensuring high-quality production output.
-
Tool tracking and performance analysis: Monitoring the usage, performance, and wear of tools over time. This data can be used to make informed decisions about tool replacement, identify opportunities for process improvement, and evaluate the cost-effectiveness of tools.
-
Disposal and replacement: Properly disposing of tools that are no longer useful or repairable and replacing them with new or refurbished ones. This ensures that the production process is not hindered by ineffective or unsafe tools.
Common tooling management challenges in manufacturing
Manufacturers encounter several challenges with tool management that can impact their efficiency, productivity, and overall operational costs.
The most common challenges include:
-
Tool maintenance and repair scheduling: Ensuring tools are properly maintained and repaired requires a systematic approach. Neglecting tool maintenance can lead to increased wear and tear, reduced tool life, and compromised product quality.
-
Tracking and inventory management: Overstocking leads to increased costs and diminished inventory capacity while understocking can cause production delays. Moreover, misplaced or lost tools can lead to unnecessary downtime.
-
Tool lifecycle management: Determining the optimal time to retire and replace tools can be difficult. Manufacturers must analyze tool performance and wear over time to make cost-effective decisions without compromising on production quality or efficiency, which can be challenging in plants with demanding production schedules.
-
Integration with production schedules: Aligning tool availability with fluctuating production schedules requires efficient scheduling and forecasting. Any misalignment can lead to idle machinery or unutilized labor.
-
Technology adoption and integration: Implementing advanced tool management solutions (e.g., software, RFID technology) is a complex process that requires a significant upfront investment. Additionally, integrating these technologies with existing systems can pose technical challenges as well as friction with workforce buy-in.
-
Training and skill levels: Ensuring staff are properly trained to use, maintain, and manage tools is essential for an effective tooling management system. Skill gaps often lead to improper tool use, increased wear and damage, and safety risks.
-
Regulatory compliance and safety: Adhering to industry regulations and ensuring worker safety, especially regarding tool handling and maintenance, adds another layer of complexity to tool management.
Technical, process, and workforce challenges can arise when implementing new tool management systems, especially if these systems require you to adapt your processes to make them work.
When choosing new tool management software, it’s important to consider the impact on your workforce. Technological change should complement and enhance your workers’ skills and abilities — not create more obstacles for them.
Tool management best practices
Successful tool management requires you to equip your workforce with the right technologies, processes, and training while emphasizing continuous improvement. Here are the best practices you can follow to streamline tooling management processes and maximize efficiency.
Implement real-time tool tracking
Using software solutions like connected workforce platforms allows you to implement real-time tracking of tools using technologies like RFID, NFC, or QR codes. Real-time tracking lets you immediately locate and update the status of every tool within the manufacturing facility, which significantly reduces the time workers spend searching for tools. It also helps in identifying bottlenecks and optimizing tool flow.
Real-time tracking capabilities ensure that tools are always available when needed — a game-changer if you’re trying to minimize downtime and improve productivity.
Adopt predictive maintenance strategies
By monitoring tool usage and wear patterns, manufacturers can schedule maintenance before failures occur, extending the life of tools and avoiding unplanned downtime. This proactive approach not only saves costs on emergency repairs but also maintains consistent production quality by ensuring tools are always in optimal condition.
To implement predictive tooling maintenance in your plant, select software with advanced data collection and analytics capabilities so you can efficiently schedule tool maintenance.
Optimize inventory management
Essential tools should always be in stock without overburdening storage with excess inventory. Digitizing inventory management with solutions like connected worker platforms allows you to automate tool reordering, enable dynamic tool tracking, and prevent excess inventory.
It also facilitates better financial planning by providing insights into tool usage trends and inventory levels, helping manufacturers minimize waste and reduce inventory costs.
Enhance training and skill development
Regularly updating tooling-related training content based on new insights and technologies keeps the workforce skilled, knowledgeable, and less prone to error. Connected worker platforms can serve as a central repository for training materials, including how-to videos, manuals, and best practices for tool usage and maintenance.
By providing workers with easy access to this information, manufacturers can make sure that tools are used efficiently and maintained properly, reducing wear and tear.
Foster a culture of continuous improvement
An effective tool management system allows room for continuous improvement. This collaborative approach encourages workers to develop and share valuable insights that can lead to continuous operational improvements. Analyzing workers’ feedback and real-time data helps you identify trends and areas for improvement, such as the need for additional training, changes in maintenance schedules, or updates to the tool inventory.
Refining tool management practices based on current data and worker feedback helps manufacturers dramatically boost efficiency and productivity.
Improve tool management with the L2L Platform
L2L’s connected workforce platform helps manufacturers of all sizes simplify tool management by empowering workers with the right information at the right times. Additionally, our platform provides an easy way for plant leaders to centralize tool information and visualize important metrics, such as inventory levels and tool conditions, in real time.
Moreover, L2L makes it easy to track and manage your workforce’s skills and certifications. This provides an easy way to assign new training modules to operators and technicians who need to learn how to use and care for new equipment.
See for yourself how L2L transforms shop floor operations — contact us today to schedule a personalized product demo!
Revisions
Original version: 5 April 2024
Written by: Evelyn DuJack
Reviewed by: Daan Assen
Please read our editorial process for more information
Subscribe to Our Blog
We won't spam you, we promise. Only informative stuff about manufacturing, that's all.



