
Connected manufacturing is one of the major pillars of Industry 4.0. If you’re familiar with connected workers, it’s easy to understand the basics of connected manufacturing. Think of it as a broad application of connected technology principles to the manufacturing process as a whole.
In this article, we’ll dive into the core technologies of connected manufacturing, the benefits of this approach, and how to overcome common challenges along your connected manufacturing journey.
What is connected manufacturing?
Unlike traditional manufacturing, connected manufacturing is a strategy that uses connected technologies — such as cloud computing, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), and real-time communication devices — to enhance a plant’s overall performance. Connected technologies improve visibility into key manufacturing processes, uncovering opportunities for improvement.
Connected manufacturing gives manufacturers a full view of their people, machines, and processes. It helps them identify what’s working and what isn’t, enabling them to implement critical changes at every level of their organization.
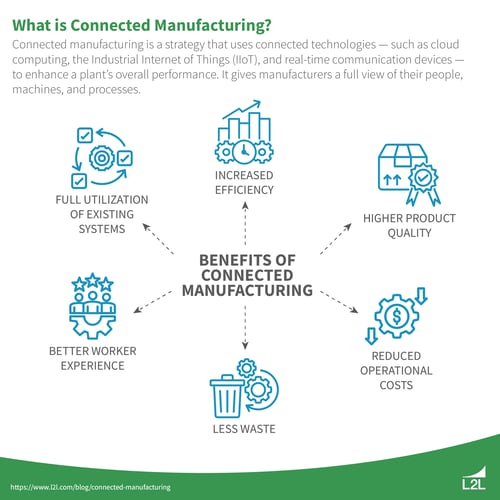
The major benefits of connected manufacturing include:
-
Increased efficiency: Connected manufacturing is designed to create efficiencies at every stage of the production process. Real-time data analytics, instant communication, automation, and full visibility into operations allow organizations to achieve maximum productivity with minimal resource consumption.
-
Better product quality: With greater visibility into production, manufacturers can spot and solve production issues faster. This results in improved product quality without loss of productivity.
-
Reduced operational costs: Since connected manufacturing technologies make facilities more efficient, long-term operating costs tend to go down.
-
Less waste: Connected manufacturing strategies, once properly implemented, result in a reduction in waste. From excess scrap to carbon emissions, most adopters of connected technologies see substantial improvements in waste metrics.
-
Better worker experience: Connected manufacturing creates a safer and less frustrating environment for frontline workers. Technologies like connected worker platforms streamline information sharing, foster better collaboration, and use data to improve workplace safety.
-
More value from existing systems: When integrated with connected technologies, your existing manufacturing systems — ERP, SCADA, CMMS, and more — can be utilized to their full potential. Connected manufacturing helps you unlock data from these systems and turn it into actionable insights.
Connected manufacturing’s benefits equip manufacturers across industries to stay flexible and agile in a volatile market. This is crucial for staying competitive in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
Technologies for creating an interconnected manufacturing environment
Creating a connected manufacturing environment involves implementing technologies from three distinct categories: machine-to-machine (M2M), machine-to-human (M2H), and human-to-human (H2H).
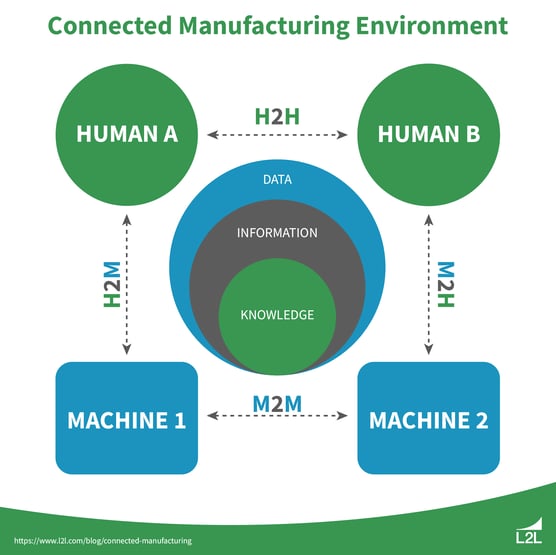
Let's break this down more below.
Machine-to-machine communication
M2M communication is a critical aspect of smart manufacturing, enabling devices and systems to exchange information and act on it autonomously without human intervention. It allows your machines to “talk” to each other on the shop floor.
IIoT devices are a prime example of M2M communication technology. For example, predictive maintenance is enabled by a network of sensors that monitor machines for abnormalities. Once they collect the data, they transmit it across the plant’s network to be analyzed by computers in real time. This IIoT-powered exchange of data enables instantaneous alerts, work orders, and other notifications to the right personnel at the right time.
M2M communication often relies on OEM-embedded devices within machines and equipment, which communicate with IIoT platforms. Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and edge computing devices are also commonly used in manufacturing M2M communication.
Machine-to-human communication and collaboration
Like M2M communication, M2H communication makes it easy for workers and machines to “talk” to one another on the shop floor. It ensures that operators, technicians, and managers are kept informed about machine status, performance metrics, alerts, and other relevant data.
M2H communication is typically facilitated by technologies like human-machine interfaces (HMI), mobile devices, and AR or VR-enabled devices. HMI simply refers to touchpoints used in human-machine interaction that display machine performance data. Dashboards, push button replacement screens, and system overview screens are common HMI applications in manufacturing.
Human-machine interaction in a factory also happens through the use of mobile devices, such as tablets and smartphones, to access machine data and control settings. For training or troubleshooting scenarios, workers may use AR or VR-powered devices and wearables.
Under a broader definition of M2H communication, cobots and humans work together, side-by-side, to accomplish repetitive tasks with optimal efficiency. Cobots can take over traditionally human functions, such as welding, assembling parts, and packing, speeding production and freeing workers to perform more complex tasks.
Human-to-human communication and collaboration
H2H communication is integral to efficient coordination, collaboration, and decision-making within the connected smart manufacturing environment. There’s no substitute for talking with your coworkers on the shop floor. That’s why communication and collaboration tools are core technologies of connected manufacturing.
For instance, connected worker solutions are designed to streamline H2H and even M2H communication using advanced technologies like data analytics, cloud computing, IIoT networks, and more. They empower frontline workers with real-time information that’s easily accessible when and where they need it.
H2H collaboration is also enabled by mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. Not only can workers use them to communicate with coworkers and supervisors across the plant, but mobile devices make it quick and easy to get help from experts outside of the facility.
Common implementation challenges and solutions
Evolving into a connected manufacturing facility is a gradual process that requires planning, patience, and flexibility. You’re bound to face challenges along the way, but overcoming them is relatively easy with the right tools and strategies.
Here are some of the most common obstacles manufacturers face during their connected manufacturing journey:
-
Integration: Before you select connected smart factory technologies, it’s crucial to ensure that your existing legacy systems are compatible with the solutions you want to integrate. Engage your IT personnel in both the technology selection and integration process to ensure that new tools, software, and devices work in harmony with current systems.
-
Cybersecurity: Another common challenge of connected manufacturing transformations is keeping your factory data safe. With increased connectivity comes an amplified risk of cyber attacks on machines, intellectual property, and even personal data. Create an effective cybersecurity strategy for your organization that includes conducting a comprehensive risk assessment and implementing a formal security governance program.
-
Data Management: Your plant generates troves of data every minute of operation. Vast amounts of data can be difficult to properly store, let alone put into action. To make sure you’re utilizing your data to its full potential, invest in the right data management solutions for your organization’s current and future needs (hint: consult your IT department). Don’t forget to include data analytics tools so you can turn insights into action on your shop floor.
-
Talent: Skilled worker retention has been one of manufacturing’s biggest challenges for the past decade. However, worker retention is crucial and can’t be solved by replacing people with machines. To keep skilled workers in your plant, create a people-first work environment by improving training programs and using technology like connected worker platforms to make work less frustrating and more fulfilling.
Creating a connected smart manufacturing workspace isn’t a linear process, but the benefits of a carefully mapped-out transformation will pay your organization dividends in the long run.
The future of connected manufacturing
Connected smart manufacturing technologies like IIoT, connected workforce platforms, and AR headsets, coupled with digital-first strategies, have transformed plants across industries. But recent advancements in factory connectivity have only scratched the surface of what’s possible.
As companies continue to standardize connected manufacturing methodologies within their facilities, emerging innovations like 5G and quantum computing promise to accelerate industrial transformation even further. 5G, for example, offers ultra-high-speed connectivity that enables faster production processes. Improved processing capabilities that come with quantum computing promise to revolutionize design, risk assessment, supply chain management, and quality control.
Further advancements in AI and machine learning (ML) will also drive the connected manufacturing evolution over the next decade. AI-powered functions like predictive analytics will become more accurate, precise, and robust, while ML will enable even faster problem-solving at every level of business.
While these innovations may seem out of reach to many manufacturers, taking steps to connect your factory floor is critical for remaining competitive. Technology is advancing exponentially, and with it, customer expectations. Setting your organization up for success now will save you operational — and financial — headaches in the near future.
Parting thoughts
Industry 4.0 has fundamentally changed manufacturing, and it’s only underscored the need for connectivity on the factory floor. Creating a connected manufacturing environment won’t just streamline processes and maximize efficiency in your facility; it will also help you attract, retain, and empower skilled workers.
Connected worker solutions like L2L give manufacturers like you a massive leg up on their competition. Our platform gives everyone in your plant a real-time picture of shop floor operations and equips frontline workers to spot and solve problems faster.
But don’t take our word for it — see L2L in action with our new virtual product tour now!
Revisions
Original version: 11 October 2023
Written by: Evelyn DuJack
Reviewed by: Daan Assen
Please read our editorial process for more information
Related Posts
Subscribe to Our Blog
We won't spam you, we promise. Only informative stuff about manufacturing, that's all.



