
In today’s manufacturing landscape, digital technology is indispensable to a successful industrial business. Digital manufacturing — a process using digital technologies to optimize, automate, and improve manufacturing operations — has fundamentally changed the trajectory of industrial production. Now, companies are answering the question, “How do I deliver the most value to our customers?” with another question: “How can I digitize my business faster?”
Despite the push toward digital manufacturing, most companies have yet to fully adopt digital manufacturing principles in their facilities. In fact, a recent L2L survey revealed that only 30% of manufacturers claimed their organizations planned to increase their spend on digital transformation.
Technology (along with customer demands) is evolving faster than most manufacturers are digitally maturing. But staying ahead of the competition requires more than taking your factory digital — you need to design your operations around the future of industrial work.
What is digital manufacturing?
Simply put, digital manufacturing is the use of advanced digital technologies, such as the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and data analytics, to optimize and automate production processes. The goal of integrating these technologies is to maximize efficiency, flexibility, and ultimately — long-term profitability.
Key technologies involved in digitizing manufacturing processes include:
-
Internet of Things (IoT): Sensors and devices connect machines and systems to gather real-time data for monitoring and control.
-
Connected Worker Platforms: Connected worker solutions integrate workers with their environments through digital technology, improving worker efficiency, safety, and productivity.
-
AI and Machine Learning (ML): These technologies enable data analysis, predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization.
-
3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing): Allows for rapid prototyping, customization, and the creation of complex parts with precision.
-
Big Data and Analytics: Data-driven insights are used to optimize processes improve quality, and enable smarter decision-making.
-
Robotics and Automation: Automated systems and robots perform repetitive tasks, improving efficiency and reducing human error.
-
Cloud Computing: A modern computing method that enables data storage, sharing, and access to software tools and analytics from anywhere, promoting collaboration and scalability.
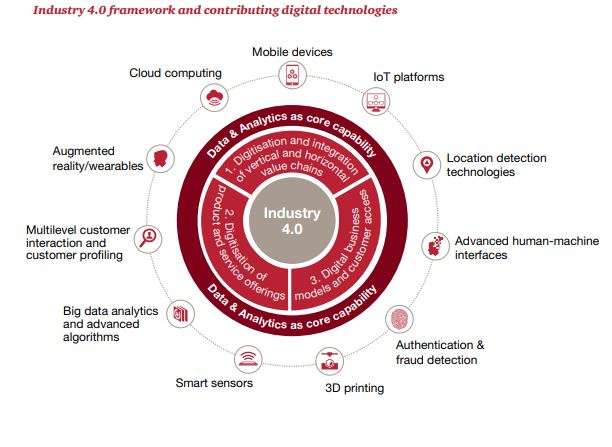
Hallmarks of Industry 4.0, these technologies are major contributors to spearheading digital transformation in manufacturing facilities. But digitizing your manufacturing facilities isn’t just about keeping up with the times. It’s essential to keep your organization future-proof.
Why are factories implementing digital manufacturing technology?
From improving OEE to increasing visibility into shop floor operations, manufacturers implement digital manufacturing technology for many reasons — from improving worker retention to improving business resilience. In fact, a recent study by Gartner reveals that 80% of CEOs are spending more on digital technology to counter current economic pressures.
Here are some of the most common goals of shifting from traditional to digital manufacturing:
-
Operational Efficiency: Enhancing operational efficiency means streamlining production processes, minimizing downtime, and eliminating as much waste as possible. Automation, IoT sensors, and real-time data analysis are key components that enable these improvements.
-
Quality Improvement: Through sensors and data analytics, manufacturers can use predictive maintenance practices to detect material abnormalities early in the production process. This allows for immediate corrective actions, ensuring that only high-quality products reach customers.
-
More Effective Workers: Digital manufacturing repositions humans at jobs where they can apply creative problem-solving. For instance, robotics and automation can do the legwork of defect detection on the assembly line while workers administer these actions and make data-driven decisions.
-
Cost Reduction: Optimizing processes, minimizing waste, and automating repetitive tasks, helps manufacturers lower operational expenses. For example, predictive maintenance powered by IoT sensors can minimize breakdowns and associated costs.
-
Agility and Flexibility: A digital factory enables greater flexibility throughout the production process, allowing manufacturers to quickly adapt to changes in product specifications or shifts in market demand. This adaptability boosts competitiveness and keeps lead times to a minimum.
-
Data-Driven Decision-Making: Manufacturers collect vast amounts of data from sensors, machines, and even workers. By analyzing this data in real time, they can make informed decisions about production, supply chain management, and resource allocation.
-
Improved Customer Experience: Manufacturers aim to provide a better customer experience through digital channels for communication, customization, and support. Customer data collected through digital touchpoints can also improve product development strategies.
Digital transformation helps manufacturers reach a wide range of goals. Moreover, digital manufacturing helps them reach their goals much faster than traditional manufacturing methods, allowing them to stay ahead of market conditions — and their competition.
Where is digital manufacturing headed?
Digital manufacturing is moving toward real applications, but it will take time to get there. Current estimates say that only about 26% of companies are already using some type of digital manufacturing — the “frontrunners.”
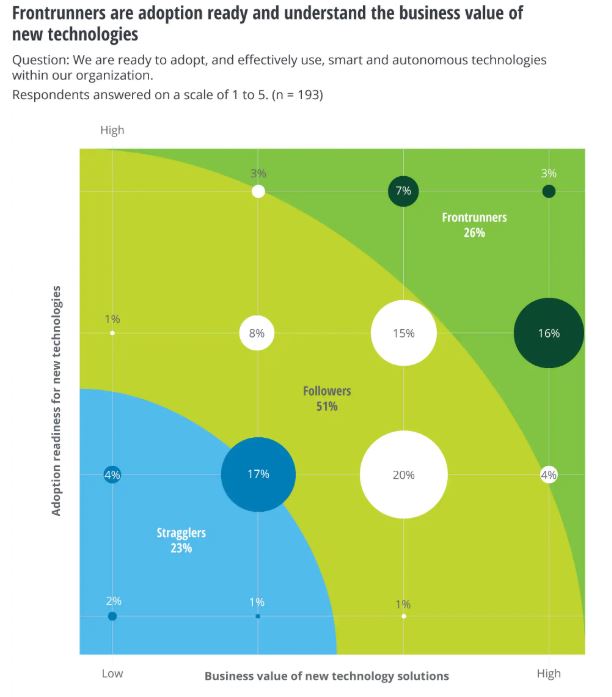
These frontrunners strongly believe in the value that adopting new technology has for digital transformation in manufacturing. Their competitive advantage is simply the fact that they’re the first players at the table.
The digital manufacturing revolution relies on five related trends emerging today:
1. Data-driven
Airbus uses digital innovation to enhance value for its customers and its technicians. Known as Skywise, Airbus’s open-data platform offers features such as fleet analysis, efficiency monitoring, and predictive maintenance. Data also drives the analytics tool on the platform, which helps the company minimize fuel consumption. So far, more than 12 airlines and 2,000 aircraft have connected to its digital platform.
2. Connected
Networked manufacturing allows for waste reduction, better predictive maintenance, and improved flexibility. It’s the customer’s demand that becomes the driver in the supply chain, as production systems will be designed to handle smaller volumes and mass-customized product portfolios.
For example, global fashion retailer Zara is using connected tools to respond even faster to customer preferences, reduce supply chain costs and empower staff members to update a store’s inventory. All it takes is waving a small, hand-held device at racks of clothing.
3. AI
AI is changing the landscape by learning what the landscape is, and then using that insight for continuous improvement. In partnership with Google, former Baidu star Andrew Ng created Landing.ai, a platform specifically focused on bringing artificial intelligence to the manufacturing industry through computer vision technology.
The platform can empower an organization’s digital maturity, prompting evolution based on a digital transformation strategy.
4. On-demand components
This trend relies on 3D printing, known as additive manufacturing. Used by Boeing to create non-flight critical hardware for military aircraft, on-demand or “Direct Digital Manufacturing” (DDM), is a way to fabricate components seamlessly.
From computer design to actual parts in hand, DDM opens up a whole new realm of possibility. Speed is just one benefit. An even more tangible advantage is the fact that it doesn’t call for an entire manufacturing line and doesn’t need retooling for new or small changes.
5. Robotics
Automation, a tenet of digital transformation in Industry 4.0, relies on robotics. This enables a level of accuracy and productivity on processes, far beyond human capability. Robotics in manufacturing also has the potential to bring in voice and image recognition to re-create human-centric tasks.
It’s manufacturing firms that will invest the most in robotics — because manufacturing businesses have the most to gain.
Start your digital transformation journey with L2L
You can’t have a digital manufacturing revolution without technology investments. Before an enterprise-wide strategy for digital transformation comes along, businesses need the software and infrastructure intended to power this change.
Yet, many manufacturers have a difficult time making this change. If you’re already struggling with daily operational challenges, how can you simultaneously develop and invest in a strategy for your digital manufacturing revolution?
In our Smart Factory eBook, we show you it’s possible. Download it today to learn how to address current production issues while paving the path forward using a proven roadmap focusing on quick ROI and targeted success.
Revisions
Original version: 27 September 2023
Written by: Keith Barr
Reviewed by: Evelyn DuJack
Please read our editorial process for more information
Related Posts
Subscribe to Our Blog
We won't spam you, we promise. Only informative stuff about manufacturing, that's all.



