
Artificial intelligence (AI) is everywhere. From Alexa (speech recognition) to Face ID (computer vision) to that chatbot you interacted with to troubleshoot an Internet issue (generative AI), AI is now ingrained in our everyday lives. This is not only true for consumers, but businesses across industries are also embracing AI's capabilities en masse.
In this article, we’ll discuss the types and applications of AI in manufacturing, the challenges of integrating AI into production processes, and the future of manufacturing AI.
The Four Types of AI in Manufacturing
Artificial intelligence in the manufacturing industry typically falls into four broad categories, depending on the technology’s rigidity and requirement for human involvement.
Here’s how PwC breaks it down:
-
Assisted intelligence: This hardwired AI technology helps humans perform tasks. It doesn’t learn from humans but rather provides guidance that enables more accurate task completion. An algorithm that analyses inventory levels falls into this category.
-
Augmented intelligence: A level up from assisted intelligence, augmented intelligence systems enhance humans’ capabilities, but they use machine learning (ML) to incorporate input from humans and other systems to get “smarter.” An example of augmented intelligence in manufacturing is AI-guided work instructions.
-
Automation: AI-driven automation involves processes that require no routine human input. Robotic process automation (RPA) is an example of automated intelligence in manufacturing.
-
Autonomous intelligence: This is the most advanced form of AI in manufacturing. Autonomous intelligence technology acts independently of human input, taking over manual and cognitive tasks that require fast adaptation to new data. One example includes self-driving warehouse vehicles.
You can use artificial intelligence for manufacturing for a wide variety of purposes. Oftentimes, you’ll need to implement AI technology from multiple categories mentioned above to maximize efficiency.
In the following section, we’ll dive into department-specific AI applications.
How Is AI Used in the Manufacturing Industry?
Every year, industrial organizations are finding more uses for artificial intelligence in manufacturing processes. AI finds unique use cases in almost every facet of manufacturing, and its adoption is projected to increase exponentially over the next decade.
Here’s how different areas of manufacturing use AI to enhance systems and processes:
Using AI for quality control
Artificial intelligence enhances quality control in a few key ways. It enables automated product inspections, visual data set analysis, and real-time quality defect detection.
For instance, machine learning algorithms can instantly identify deviations from quality specifications. Predictive maintenance systems use AI to detect potential equipment failures before they occur. Applications like these reduce human error and elevate adherence to quality standards.
Using AI in product development and engineering
Product development and engineering teams often use AI to streamline processes such as design, testing, and prototype optimization.
Manufacturers can speed up product development cycles by using AI-driven design tools, which create innovative designs while assessing their real-world feasibility.
Engineers and developers can also use machine learning applications to analyze prototyped and existing products for defects and suggest solutions for improvements.
Using AI in procurement
AI is often used to streamline different parts of the manufacturing procurement process. It can automate portions of the procure-to-pay (p2p) process and other tedious activities, such as invoice handling.
Algorithms can detect irregularities in the supply chain, market prices, and even compliance. AI technology even offers manufacturers benefits like guided buying and supplier risk management.
Order management guided by AI
Artificial intelligence streamlines the order management process through automation, inventory tracking, and demand forecasting. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data to predict demand and optimize inventory levels accordingly, which helps manufacturers avoid excess or insufficient stock.
AI-driven analytics can also be applied to customer and supplier interactions and buying habits. This helps manufacturers maintain high customer satisfaction with relatively little effort.
AI applications in maintenance
One of the most popular applications of AI in manufacturing is predictive maintenance. Predictive maintenance is a proactive approach to equipment upkeep that uses data analytics to gather machine data and interpret the data’s “story” through machine learning.
Known as predictive analytics, this process allows maintenance teams to see patterns and irregularities that could eventually lead to mechanical failures. This helps manufacturers take action before a costly breakdown happens.
AI for logistics planning
Manufacturing organizations can use AI to optimize logistics planning activities. AI algorithms aid in choosing efficient and sustainable routes, managing inventory, and reducing costs associated with shipping.
Using machine learning, manufacturers can predict future demand and adjust inventory levels accordingly. Overall, incorporating AI into logistics planning leads to greater supply chain visibility, shorter lead times, and less waste.
Using AI for supply chain management
Artificial intelligence is transforming supply chain management for manufacturers. Manufacturers can track shipments in real time, predict demand fluctuations, navigate disruptions, and maintain stable inventory levels. Additionally, natural language processing aids in supplier communication and even extracting information from digital documents.
The Challenges of Implementing AI in Manufacturing
Although artificial intelligence has revolutionized critical manufacturing processes, it’s still a new, evolving branch of technology. Simply put — implementing AI solutions comes with its fair share of challenges.
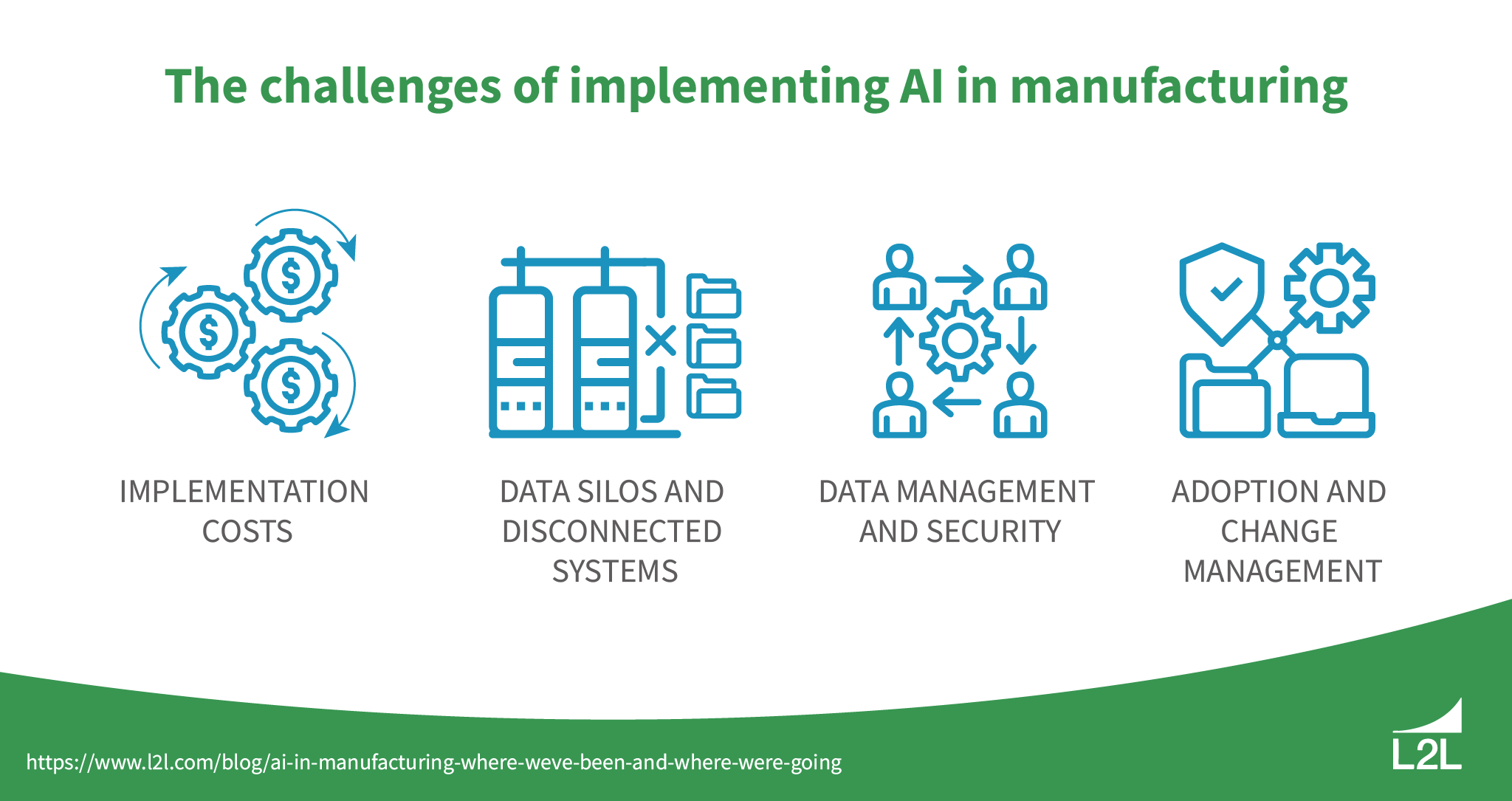
Here are the most common hurdles industrial companies face when implementing AI technology:
-
Implementation costs: Like most advanced solutions, AI for manufacturing is expensive to configure and update, and many smaller manufacturers lack sufficient funds to purchase the AI solutions they want. However, AI implementation can be done in stages and doesn’t require a complete system overhaul, depending on how you plan to use it.
-
Data silos and disconnected systems: If you have trouble sharing data across your organization because it’s locked up in disparate systems, you’ll have an even harder time implementing AI solutions. Seamless data sharing is critical for getting the most out of your manufacturing AI. Make sure you remove all barriers to effective collaboration before introducing new, advanced technologies.
-
Data management and security: With IoT sensors and devices all across production floors, manufacturers can generate massive volumes of data. You need to set a proper infrastructure and data management practices to clean and feed that data to your AI algorithms. And, as you go digital, you should have a solid data security strategy to minimize increasing cybersecurity risks.
-
Adoption and change management: Whether workers are intimidated by the new technology or lack the resources to master it, it’s crucial to lay the proper training foundation for seamless AI adoption. Your new solutions should enhance worker productivity — not hinder it.
What Is the Future of AI in Manufacturing?
In the past decade, we’ve witnessed nothing short of an AI revolution in the industrial sector. This revolution is only predicted to accelerate in the coming years, driven by emerging innovations like the metaverse, generative AI, and advanced robotics.
There’s been significant buzz around the concept of the industrial metaverse over the last few years. In manufacturing, this branch of technology — focused on integrating physical and digital experiences — has brought forth innovations like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) solutions on the shop floor. VR headsets, smart glasses, and digital twins will continue to help manufacturers speed up training and product development processes as they become standardized in the future.
Generative AI is also poised to transform manufacturing operations
in the near future. This AI subset lets developers create product designs virtually from scratch using advanced design algorithms. These designs will then undergo testing in the metaverse. As a result, we’ll see dramatically accelerated product development and testing. Plus, this approach to development will help manufacturers cut waste and costs.
AI-enabled robots are also predicted to maximize efficiency and quality in the future. Equipped with sensors, generative AI, and data-driven computation, these robots will perform repetitive tasks with more precision and speed than ever before.
In this video (4:06), John Fishell, VP of Product at L2L, discusses the future of AI in manufacturing and its impact on frontline workers.
Empower Your Workforce with AI
These are only a handful of the changes AI will bring to discrete manufacturers in the near future. And the best part? You can take advantage of AI in your manufacturing facility right now. With connected manufacturing operations platforms like L2L, your workforce can reap the benefits of more streamlined, less frustrating processes, while you can see increased productivity, efficiency, and profits in months, not years.
See how you can use AI and other smart manufacturing technologies to transform your plant operations when you take our Product Tour!
Revisions
Original version: 19 October 2023
Written by: Evelyn DuJack
Reviewed by: Daan Assen
Please read our editorial process for more information
Related Posts
Subscribe to Our Blog
We won't spam you, we promise. Only informative stuff about manufacturing, that's all.



